Eating late at night can disrupt your digestion, slow down metabolism, and affect sleep quality. This article explores the health risks of late-night eating and provides tips on how to break the habit for improved overall health.
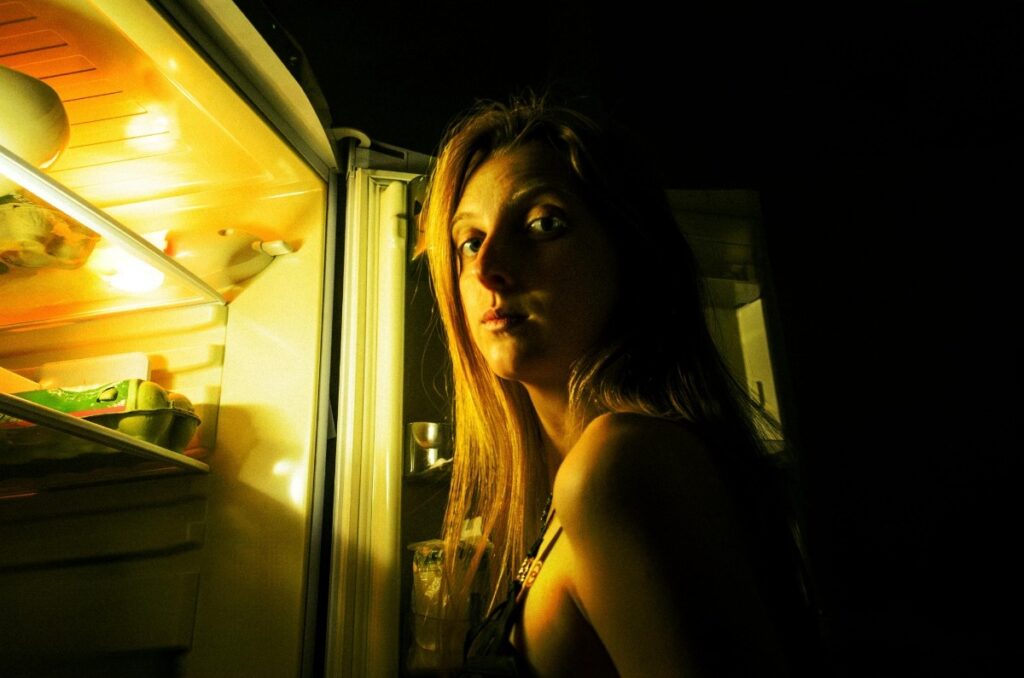

Late-night meals have become a common habit, especially with changing work schedules, long screen time, and irregular sleep routines. However, eating close to bedtime can have several negative effects on your health. While hunger at night may feel normal, it’s important to understand how late-night eating impacts your body over time. Here’s how late-night eating impacts your health:
Disrupts Digestion
The body’s digestive system works best when upright and active. Eating late at night, especially heavy or spicy foods, can cause the stomach to produce more acid. This increases the risk of acid reflux, bloating, and indigestion—symptoms that can be uncomfortable and disturb your sleep. When you lie down soon after eating, it becomes harder for the stomach to process food properly, leading to discomfort and poor digestion.
Slows Down Metabolism
Your body follows a natural rhythm called the circadian clock. This clock helps manage sleep, digestion, and metabolism. Eating at night goes against this rhythm, which can confuse the body and slow down how it uses energy. As a result, food eaten late is more likely to be stored as fat instead of being burned for energy. Over time, this can lead to unwanted weight gain.
Raises Blood Sugar Levels
Late-night eating can cause blood sugar levels to rise overnight, especially if the food is high in carbohydrates or sugar. This can make it harder for the body to maintain a healthy blood sugar balance, increasing the risk of insulin resistance. People who often eat late are more likely to face issues like high fasting sugar levels, which may lead to type 2 diabetes in the long run.
Affects Heart Health
Frequent late meals may also increase the risk of high cholesterol and high blood pressure. Studies have shown that eating late, especially unhealthy snacks, can lead to higher levels of triglycerides and bad cholesterol. These changes can put extra pressure on the heart, increasing the risk of heart-related problems over time.
Disturbs Sleep Quality
Eating late can affect your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. When the body is still busy digesting food, it may not fully relax for deep sleep. Certain foods can also increase body temperature or trigger restlessness, making it harder to get restful sleep. Poor sleep has its own set of health risks, including fatigue, low mood, and weakened immunity.
Increases Risk of Weight Gain
Late-night eating is often linked to higher calorie intake. People are more likely to choose high-fat, salty, or sugary foods at night, especially when eating out of stress or boredom. This extra energy, combined with less physical activity in the evening, can lead to weight gain over time.
Tips to Avoid Late-Night Eating
- Eat dinner earlier: Try to have your last meal at least 2 to 3 hours before bedtime.
- Stay hydrated: Sometimes, thirst is mistaken for hunger.
- Choose lighter evening meals: Avoid fried, spicy, or heavy foods at night.
- Plan your meals: A regular eating schedule during the day reduces the urge to eat at night.
- If you’re hungry late at night: Choose a light, healthy option like fruit, a few nuts, or low-fat yogurt.
Final Thought
While an occasional late-night snack might not cause harm, making it a daily habit can lead to digestive issues, poor sleep, weight gain, and long-term health risks. Paying attention to when you eat is just as important as what you eat. By making small changes in your routine and avoiding food close to bedtime, you can support better digestion, sleep, and overall health.
Also Read: Super Seeds for Overall Health: Benefits and Easy Ways to Add Them to Your Diet
Also Read: 10 Healthy Alternatives to Maida for Nutritious Cooking
Also Read: Health Benefits of Fruit Leaves: Natural Ways to Control Blood Sugar & Reduce Stress